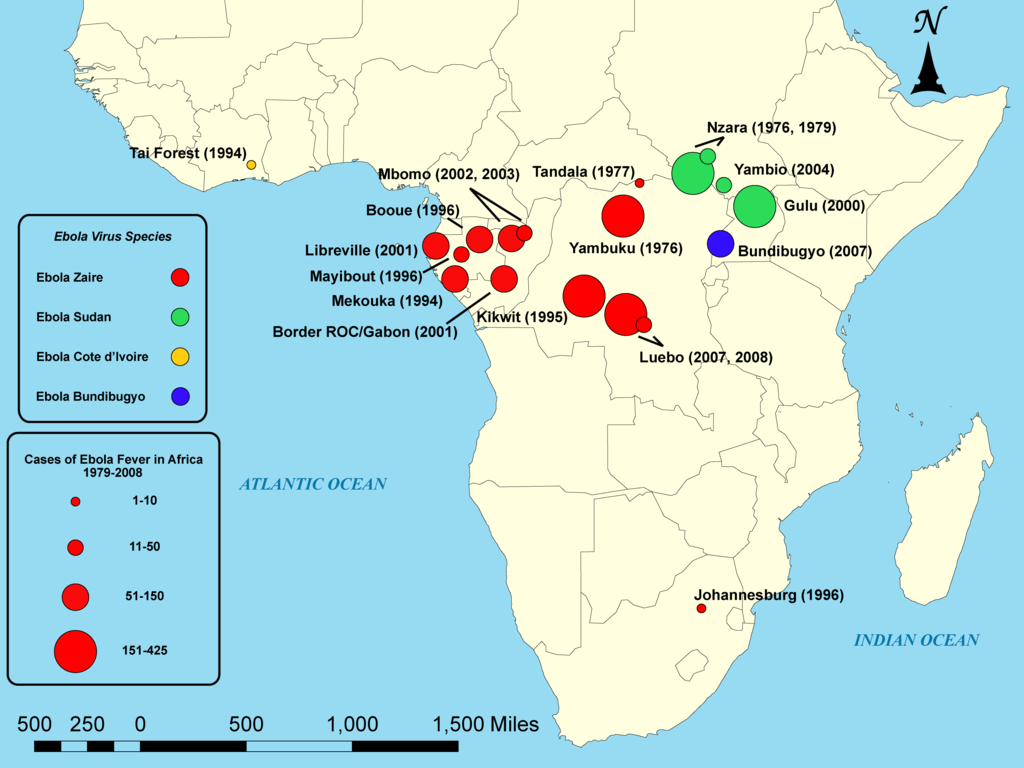
The Ebola virus was first isolated and identified to 1976 in the Democratic Republic of Congo. This virus has been found to have an average mortality rate of 88 percent in humans, one of the highest recorded. Since its initial discovery, cases of Ebola fever have been identified and quarantined across central Africa.
The virus is spread by contact of bodily fluids and blood from others who are infected. Currently there are no documented cases of the virus spreading through the air. When this virus is contracted, individuals will start to show symptoms such as muscle pain, fever, headache or sore throat 2 days to 3 weeks later. This will be followed by rash, vomiting, diarrhea, decrease in kidney and liver function as well as internal and external bleeding. Prevention of these diseases focuses on decreasing the spread of the virus from animals to humans as there is not currently a treatment for this disease.
Ebola Virus Disease History
2014 Ebola Outbreak in West Africa
According to the most recent CDC outbreak information the countries of Nigeria, Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone are seeing one of the largest outbreaks of Ebola in world history. The Emergency Operations center is providing assistance and public health experts are working to expand resources to help control the outbreak. As of 20th August, more than 1400 people have died.
2012 Ebola Outbreak in Uganda (December)
In December 2012, 7 cases of Ebola were confirmed in the Luwero District of Uganda which caused 4 deaths. The Ministry of Health diagnosed and managed the outbreak with assistance from the Viral Special Pathogens Branch. The total numbers from this outbreak are expected to change.
2012 Ebola Outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo (November)
The DRC Ministry of Health declared an outbreak of Ebola in the Province Orientale on November 26, 2012. This outbreak included 77 cases confirmed by the CDC lab in Uganda which included 36 confirmed cases, 17 probable cases, 36 deaths and 24 suspected cases. The Public Health Agency of Canada provided additional diagnostic support for this outbreak.
2012 Ebola Outbreak in Uganda (July)
In July 2012, an outbreak of Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever in Kibaale Uganda was confirmed by the Uganda Ministry of Health. This included 24 probable human cases which are being researched at the Uganda Virus research Institute as well as the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention via blood sample. This outbreak has 11 confirmed patients with 4 deaths.
2011 Ebola Case in Uganda (May)
In May 2011 an outbreak of Ebola hemorrhagic fever was confirmed in the Luwero district of Uganda by the Ugandan Ministry of Health. Tests for the virus on blood samples confirmed the outbreak at the Uganda Viral Research Institute. To date, no additional cases have been reported.
2008 Ebola-Reston Virus Was Detected in Pigs in the Philippines
In October 2008 samples of tissue from pigs from the Philippines was tested by the Foreign Animal Disease Diagnostic Laboratory. These samples were taken from Manila where swine pathogens of the Ebola virus were identified using molecular analysis. This was the first time the Reston version of the virus was identified in pigs. An ongoing search is commencing to ensure that this virus was not spread to humans.
2007 Ebola Outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo
In August 2007 the Kasai Occidental Province was struck with a disease of unknown origins. Samples from the victims were sent to the CDC Special Pathogens Branch as well as the Centre International de Recherches Medicales de Franceville. Real time testing confirmed these cased to be from the Ebola virus, though the presence of other pathogens implies that additional diseases may have been present. This outbreak had a confirmed 249 cases resulting in 183 deaths.
2004 Ebola Outbreak in South Sudan
The World Health Organization confirmed 20 cases of Ebola hemorrhagic fever in Yambio County of south Sudan in 2004. This outbreak included 5 deaths which were studied by the Kenya Medical Research Institute and the Centers for Disease control. It was also confirmed that the strain which caused the outbreak was one previously known to cause human disease.
2003 Ebola Cases in the Democratic Republic of Congo
In 2003 several cases of Ebola hemorrhagic fever syndrome were confirmed by the World Health Organization Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response team in the Republic of the Congo.
2002 Ebola Outbreak in Gabon and Republic of the Congo
In May 2002, an outbreak of Ebola hemorrhagic fever was confirmed in the Ogooue Ivindo province by the Gabonese Ministry of Health and the World Health Organization. A response team was sent to this area and neighboring villages in the Republic of the Congo.
2001 Ebola Outbreak in Uganda
An outbreak of Ebola hemorrhagic fever which occurred over 42 days occurred in Uganda. It was officially declared over on February 27, 2001 after a period of time considered twice the maximum incubation period when no new cases were reported. Between October 2000-February 2001 the World Health Organization partnered with the CDC to help control the outbreak.
|
Chronology of Ebola Outbreaks |
|||||
|
Year |
Country |
Cases |
Deaths |
Fatality Rate |
Ebola virus species |
|
1976 |
Democratic Republic of Congo |
318 |
280 |
88 percent |
Zaire |
|
1976 |
Sudan |
284 |
151 |
53 percent |
Sudan |
|
1977 |
Democratic Republic of Congo |
1 |
1 |
100 percent |
Sudan |
|
1979 |
Sudan |
34 |
22 |
65 percent |
Sudan |
|
1994 |
Gabon |
52 |
31 |
60 percent |
Zaire |
|
1994 |
Cote d’lvoire |
1 |
0 |
0 percent |
Tai Forest |
|
1995 |
Democratic Republic of Congo |
315 |
254 |
81 percent |
Zaire |
|
Jan-Apr 1996 |
Gabon |
31 |
21 |
68 percent |
Zaire |
|
Jul-Dec 1996 |
Gabon |
60 |
45 |
75 percent |
Zaire |
|
1996 |
South Africa (ex-Gabon) |
1 |
1 |
100 percent |
Zaire |
|
2000 |
Uganda |
425 |
224 |
53 percent |
Sudan |
|
2001-2002 |
Gabon |
65 |
53 |
82 percent |
Zaire |
|
2001-2002 |
Congo |
59 |
44 |
75 percent |
Zaire |
|
Jun-Apr 2003 |
Congo |
143 |
128 |
90 percent |
Zaire |
|
Nov-Dec 2003 |
Congo |
35 |
29 |
83 percent |
Zaire |
|
2004 |
Sudan |
17 |
7 |
41 percent |
Sudan |
|
2005 |
Congo |
12 |
10 |
83 percent |
Zaire |
|
2007 |
Democratic Republic of Congo |
264 |
187 |
71 percent |
Zaire |
|
2007 |
Uganda |
149 |
37 |
25 percent |
Bundibugyo |
|
2008 |
Democratic Republic of Congo |
32 |
14 |
44 percent |
Zaire |
|
2011 |
Uganda |
1 |
1 |
100 percent |
Sudan |
|
2012 |
Uganda |
24 |
17 |
71 percent |
Sudan |
|
2012 |
Uganda |
7 |
4 |
57 percent |
Sudan |
|
2012 |
Democratic Republic of Congo |
57 |
29 |
51 percent |
Bundibugyo |
Picture that shows more: