Aquatenic urticaria is a rare form of physical urticaria. This condition causes a rash or hives to appear whenever the patient comes in contact with water. Itching and pain may also be present. This condition will appear regardless of the condition or temperature of the water, though there must be no skin lesion present to differentiate this condition from aquagenic pruritus or aquadynia. Aquagenic urticaria tends to affect women more than men, though infantile patients are equally susceptible to this condition. Patients going through puberty are the most likely to manifest symptoms of this condition.
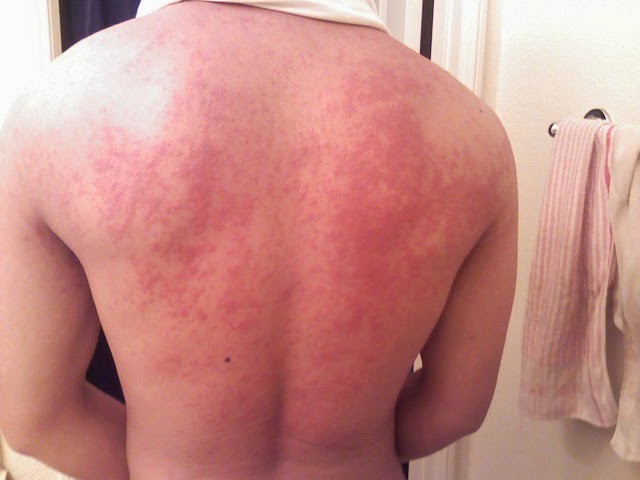
What Are the Symptoms?
Symptoms are typically skin based. The skin will itch or burn after you expose yourself to water. Within 1 to 15 minutes of this exposure hives, rash or erythema may appear. Within 10-120 minutes lesions may develop which can be quite painful. In some cases difficulty swallowing, wheezing or subjective respiratory distress will occur after drinking water.
What Causes It?
- Symptoms can occur after bathing, swimming, or walking in the rain. In some cases the skin may even break out when they sweat or emit tears. The solvents in the water or the temperature do not appear to influence the aquagenic urticaria reaction.
- Lactose intolerance appears to increase the risk of developing the disease. A familial pattern appears to coexist due to this disease's location on chromosome 2q21.
- Females that have siblings that suffer from Bernard Soulier syndrome appear to have a significantly higher chance of developing the condition. This disease increases bleeding time by altering the body's platelet count. This disease appears to be caused by a mutation on chromosome 3 which damages the body's von Willebrand factor receptor.
- Diseases such as polymorphous, atopy, cholinergic urticarial, light eruption, HIV infection as well as Bernard-Soulier syndrome appear to have a correlation with the appearance of aquagenic urticaria as well.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of aquagenic urticaria will begin with an evaluation of the patient's clinical history looking for any signs of what might be causing this severe reaction. The patient will then be put to a water treatment test where water will be applied to the upper body for 30 minutes. Water may be placed directly on the skin or a soaked paper towel may be applied. In many cases distilled water, tap water and saline will be used to check for a difference in reaction. After this is removed the skin will be checked for a reaction for the next 10-15 minutes.
Because Aqugenic Urticaria frequently accompanies other types of physical urticaraia, the doctor may perform tests to check for these other conditions. In ice cube may be placed on the forearm for a few minutes to check for cold urticarial, exposure to a hot bath will be used to check for Cholinergis urticaria and the lesions will be inspected to determine the root cause of their appearance.
How Can It Be Treated?
There is no treatment that will rid the patient of symptoms. Most treatments are used to lessen the effects of the disease to promote more comfort when the body must come in contact with water.
- Oral antihistamine- Antihistamines such as hydrochloride, hydroxyzine, terfenadine and cyproheptadine have frequently been used to reverse or minimize the effects of aquagenic urticaria. The therapeutic response to these medications will vary from patient to patient and the benefits of applying a histamine antagonist to the skin has not been found to create a direct link to the minimization of water based urticaria effects.
- Topical corticosteroids- Parenteral corticosteroids have been used to help treat aquagenic uricaria in the past. The actual effect of this medication and its benefits are not clear at this time.
- Epinephrine- Patients with severe bouts of urticarial that appear to be acute will frequently use this medication to help decrease the appearance of cutaneous vasodilation. This can also help inhibit mast cell degranulation which may contribute to the presence of aquagenic urticaria.
- PUVA therapy- In one test a 21 year old woman was given PUVA therapy four times a week in increased doses to help manage the symptoms. As the dosage was increased the lesions and itching caused by the disease disappeared.
- Ultraviolet radiation- Radiation is commonly used alongside antihistamines to help rid the patient of lesions and outbreaks caused by aquagenic urticaria. This therapy will cause thickening of the epidermis which can prevent water from penetrating this layer and interacting with the cells underneath. Ultraviolet therapy may also cause mast cells to limit their response to stimuli and immunosuppression which can help prevent these reactions.
- Stanazolol- Treatments for the human immunodeficiency virus or HIV have been found to help with the symptoms of Aqugenic Urticaria as well.
- Capsaicin - This medication is often used for producing Zostrix, a cream applied to lessen pain that caused by aquagenic urticaria.
- Barrier methods- In some circumstances and oil in water solution or emulsion cream can be applied to the skin to protect it from water exposure while washing or performing aquatic activities. There does not appear to be a side effect to this method and the application is easier than many other options. Doctors will also recommend that these patients use physical barriers such as an umbrella or protective clothing to avoid contact with water to protect patients from potential outbreaks. Activities such as swimming or visiting a water park will also need to be avoided to minimize the risk of an outbreak.
