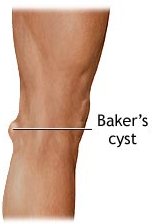
 A Baker’s cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a cyst which is associated with a person’s knee. The protruding cyst is filled with a fluid-like substance, which may appear at the back of the knee. A striking pain might be experienced when the knee is stretched or bent, or during an attempt of physical activity. In general terms, Baker’s Cyst develops when the cartilage tissues get teared up. It may also appear in people who might be suffering from arthritis. In both scenarios, the knee tends to produce additional fluid, which causes the emergence of Baker’s Cyst. These developments are truly uncomfortable and treatment provides an adequate level of relief to people suffering from Baker’s Cyst.
A Baker’s cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a cyst which is associated with a person’s knee. The protruding cyst is filled with a fluid-like substance, which may appear at the back of the knee. A striking pain might be experienced when the knee is stretched or bent, or during an attempt of physical activity. In general terms, Baker’s Cyst develops when the cartilage tissues get teared up. It may also appear in people who might be suffering from arthritis. In both scenarios, the knee tends to produce additional fluid, which causes the emergence of Baker’s Cyst. These developments are truly uncomfortable and treatment provides an adequate level of relief to people suffering from Baker’s Cyst.
How to Recognize a Baker’s Cyst
The most generic symptoms of a Baker’s cyst include the tightness of the skin around the back of the knee, a prominent swelling visible around the upper calf area, and associated pain which might be experienced once the knee is bent or straightened. In some severe cases, the pocket retaining the fluid might puncture and it may further drain in the lower leg’s tissues. As a result, prominent swelling and redness may be visible in the underlying area of the lower leg.
Probable Complications of Baker’s Cyst
In case the fluid pocket disrupts and the cystic fluid spreads around the calf area, such symptoms must not be overlooked. You might experience striking pain and redness around the calf region, as seen during a blood clot in a vein. If the symptoms prevail, it is recommended to give your knee and leg immediate medical attention to prevent it from worsening.
When to See the Doctor
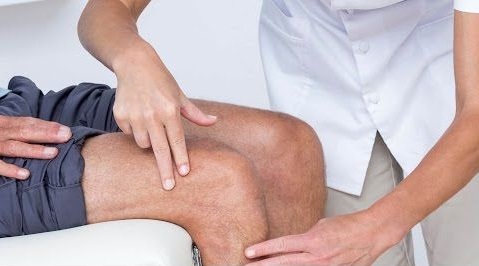 If the Baker’s cyst does not diminish after a period of time, or you experience prevailing symptoms, then it is recommended to get your knee inspected by a doctor. The doctor might ask about the symptoms you are experiencing, and questions related to your present health, such as whether you have arthritis or other related ailments. The doctor may also recommend an ultrasound or an MRI to further investigate the underlying symptoms. This might be also required to rule out the possibility of a conditions related to tumor or an aneurysm as probable causes of symptoms.
If the Baker’s cyst does not diminish after a period of time, or you experience prevailing symptoms, then it is recommended to get your knee inspected by a doctor. The doctor might ask about the symptoms you are experiencing, and questions related to your present health, such as whether you have arthritis or other related ailments. The doctor may also recommend an ultrasound or an MRI to further investigate the underlying symptoms. This might be also required to rule out the possibility of a conditions related to tumor or an aneurysm as probable causes of symptoms.
Causes of Baker’s Cyst
Baker's cyst can be caused by a number of factors.
- It can develop if a person has an injury on the leg or knee during sports or any other physical activities.
- It may also develop in people who are suffering from osteoporosis because this condition is related to aging and the wear and tear process of the bones is associated with knees, hips and toes.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, the inflammation and thickening of joints due to an aggressive immune system, might also lead to the occurrence of Baker’s Cyst.
- People with gout are also at a risk of developing Baker’s Cyst.
- It has been observed through research that women tend to be more prone to Baker’s Cysts than men, since they are at higher risks of developing osteoporosis and rheumatic arthritis.
- Also, this may appear in people who are aged above 40. Yet, the Baker’s cyst has also been observed in children.
Tips to Recover from Baker’s Cyst
Once you have been diagnosed with Baker’s cyst, you can use the following strategies to recover from its symptoms more effectively.
|
What to Do |
Description |
|
Adopt the R.I.C.E principle |
The complete form of this principle is rest, ice, compression and elevate. You need to give adequate rest to your leg. Ice the inflammation surrounding the cyst. Apply compression on the knee with the help of a sleeve, brace or wrapped cloth. And elevate your leg as much as possible, especially during night time. |
|
Knee support |
Since you are required to help your knee in getting as much rest as possible, you can use support in the form of a crutch, cane or walker. You might want to move around with such support so that it doesn’t burden the knee too much. |
|
Proper bandage |
If you have bandaged the area, make sure it is not fastened too tightly. Otherwise, swelling might appear around the bandage. |
|
Weight control |
Maintain your weight for a healthy lifestyle and ask for recommendation on how much weight you can sustain. Besides emphasizing too much weight on your knee could worsen the symptoms, so do not put too much stress on your knee. |
|
OTC drugs |
You can buy pills that will relieve the pain associated with the cyst, including Advil, Motrin or Aleve. |
|
Physical workout |
You can discuss with your doctor on the level of physical activity you should perform, and what kinds of workout can risk the overall health of your knee. |
Medical Treatment for Baker’s Cyst
Baker’s cyst can disappear on its own, and no treatment might be needed for it. But in cases when the symptoms have prevailed for a long period, or its reoccurrence has been observed, then the doctor might recommend one of the following solutions: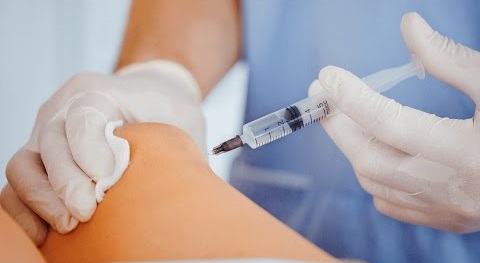
- If the cyst is extensive and painful at the same time, the doctor may infuse corticosteroid in your knee, which will help in settling the inflammation and easing out the pain. Such an infusion might prevent the pain, but it does not contribute in stopping the cyst from resurfacing again in future.
- Needle aspiration may also be performed on the cyst to drain out the fluid penetrating within it. This may be done with the sophisticated guidance of an ultrasound.
- The cyst can also be treated with the help of regular physical therapy, icing, crutches or compression pads. This process will help in reducing the symptoms over a period of time. It will also enable the surrounding muscles to retain their movement and conserve the knee functionality.
